Magento offers a fair amount of shipping options out of the box, but we often find ourselves customizing this particular core functionality due to specific needs of our clients.
In this post we will show you how to disallow shipping to specific countries and we will do it on a product level. Let’s get started!
Adding product attribute
Since the configuration will be done per product, first thing we need to do is programmatically create new product attribute. In our custom module we will add following setup script:
<?php
/* @var $installer Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Setup */
$installer = $this;
$installer->startSetup();
$installer->addAttribute(
Mage_Catalog_Model_Product::ENTITY,
'shipping_restriction',
array(
'type' => 'varchar',
'group' => 'General',
'input' => 'multiselect',
'label' => 'Disallow Shipping to',
'source' => 'inchoo_shippingrestriction/attribute_source_country',
'backend' => 'inchoo_shippingrestriction/attribute_backend_country',
'global' => Mage_Catalog_Model_Resource_Eav_Attribute::SCOPE_WEBSITE,
'apply_to' => 'simple,configurable,bundle,grouped',
'required' => false
)
);
$installer->endSetup();You will notice that our attribute has custom backend and source models and that we apply it only to product types which require shipping method.
First let’s take a look at our source model. For those that are not familiar with source models, their purpose is to fetch data for attribute. In our case it is a list of countries.
<?php
class Inchoo_ShippingRestriction_Model_Attribute_Source_Country
extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Source_Abstract
implements Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Source_Interface
{
/**
* Get list of all available countries
*
* @return array|mixed
*/
public function getAllOptions()
{
$cacheKey = 'DIRECTORY_COUNTRY_SELECT_STORE_' . Mage::app()->getStore()->getCode();
if (Mage::app()->useCache('config') && $cache = Mage::app()->loadCache($cacheKey)) {
$options = unserialize($cache);
} else {
$collection = Mage::getModel('directory/country')->getResourceCollection();
$options = $collection->toOptionArray();
if (Mage::app()->useCache('config')) {
Mage::app()->saveCache(serialize($options), $cacheKey, array('config'));
}
}
return $options;
}
}Next we will look at our backend model. Purpose of backend model is to perform various actions on data that is stored in our attribute. For example we can validate data, modify before saving/after loading, etc. In our case we will use it to convert data from array (because we get array on input) to string before it is saved and other way around after our data is loaded.
<?php
class Inchoo_ShippingRestriction_Model_Attribute_Backend_Country
extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Abstract
implements Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Interface
{
public function beforeSave($object)
{
$attrCode = $this->getAttribute()->getAttributeCode();
$object->setData($attrCode, implode(',', $object->getData($attrCode)));
return $this;
}
public function afterLoad($object)
{
$attrCode = $this->getAttribute()->getAttributeCode();
$object->setData($attrCode, explode(',', $object->getData($attrCode)));
return $this;
}
}Once the attribute has been created, it will appear on the product edit page under General tab.
Here is what it looks like:
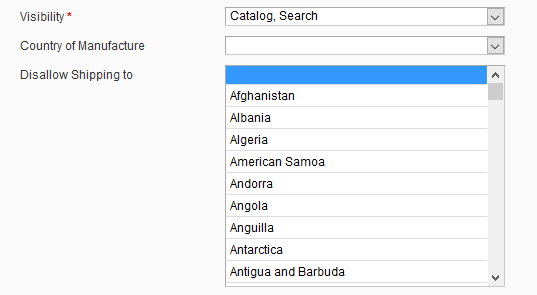
Validating shipping address
Now that we can configure our products to block shipping for specific countries, we have to implement logic which takes customer’s cart items, compares them against entered shipping address and decides if customer is eligible to select shipping method and complete the checkout process.
We cannot run our code immediately after the product was added to cart because there is no guarantee that we will have shipping address at this point. Instead, we have to wait for customer to start the checkout process.
With that in mind, we will implement our code by class rewrite method. We will rewrite Mage_Shipping_Model_Shipping class and modify its collectRates method. It seems like a good place since we have access to customer’s shipping address, all the cart items and we can control which shipping methods are returned (in our case it will be either all or none).
<?php
class Inchoo_ShippingRestriction_Model_Shipping extends Mage_Shipping_Model_Shipping
{
public function collectRates(Mage_Shipping_Model_Rate_Request $request)
{
if ($this->isShippingRestriction($request)) {
return $this;
}
return parent::collectRates($request);
}
/**
* Check if shipping restrictions apply
*
* @param Mage_Shipping_Model_Rate_Request $request
* @return bool
*/
public function isShippingRestriction(Mage_Shipping_Model_Rate_Request $request)
{
$options = array();
/** @var Mage_Sales_Model_Quote_Item $quoteItem */
foreach ($request->getAllItems() as $quoteItem) {
$options = array_merge(
$options,
explode(',', $quoteItem->getProduct()->getShippingRestriction())
);
}
return in_array($request->getDestCountryId(), $options);
}
}You may notice that following line
$quoteItem->getProduct()->getShippingRestriction()does not return any data at first. This is because Magento does not copy all the attribute data from product once it converts it to quote (cart) item. Luckily for us, Magento provides a mechanism to include additional attributes, all we need to do is write a few lines of XML.
The following code should be placed in your config.xml file inside <global> node:
<sales>
<quote>
<item>
<product_attributes>
<shipping_restriction/>
</product_attributes>
</item>
</quote>
</sales>Conclusion
Adding the config lines was the last piece of puzzle. Basic functionality is now implemented, but obviously there is always room for improvement, especially on frontend, in terms of notifications and error messages for customer. This is something we will leave as an exercise for reader since main focus of this article was on backend implementation.
Happy coding! 🙂