Blackhat SEO branded keywords hijacking. Say whaaaat?! Oh, yes! Read about blackhat cloacking technique used mainly by scammers where your branded keywords are used to drive traffic to scam ecommerce sites.
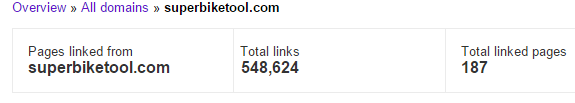
It all started with a large number of new external links pointing to one of our client’s websites and we’ll call them a “victim” from now on. 38 000+ links pointing to just one page, and there were plenty of others links pointing to other pages as well. All in all – more than 500 000 new external links.
Links look fishy at first sight:
- all links come from a domain of a topic completely unrelated [bike parts/tools] to victim’s website [fashion retailer]
- there’s a layer of redirection in the game
- links redirect to a COMPETITOR’s website [in this case – a scam website with products related to victim’s website]
- GET parameter resembles URL path structure of victim’s website
- source domain is most likely hacked and being used as a host [infected host]
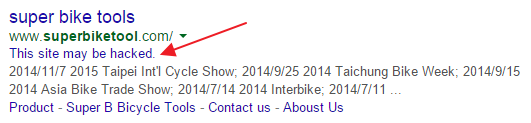
In this particular case, even Google is aware of the fact that the infected host is hacked:
It’s time for a bit of HTTP analysis…
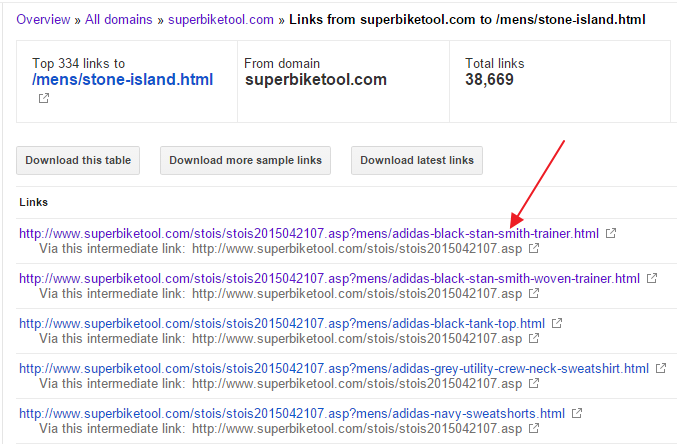
One URL is picked and analyzed:
As Google/GWT see it, it should have a link back to a valid victim’s URL: http://www.example.com/brand-name.html
But instead, it redirects to a scam website [don’t buy anything from this SCAM site, you’ll see later why ;-)]:
http://www.stoneislandsshop.com/?keyword=http%3A%2F%2Fwww%2Esuperbiketool%2Ecom%2Fstois%2Fstois2015042107%2Easp%3Fmens%2Fadidas-black-stan-smith-trainer%2EhtmlOf course, there are no backlinks to victim’s site on scam site. But how did Google got confused to properly index infected host’s URL and list that URL as a backlink?!
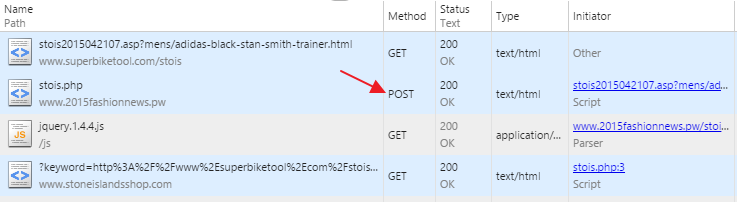
Let’s analyze redirects, or better say “redirects” step by step:
- [POST redirect] a link on infected host redirects using POST method to intermediate host [POST is important, as it stops Google from passing through]
- [CLOAKING] intermediate host [server side PHP script] then checks whether user-agent has “googlebot” – if so, it sets cookie. As page is rendered – it then redirects a client to a scam website using jQuery redirect [client side Javascript] or to a Google is user-agent is “googlebot”
<script src="js/jquery.1.4.4.js" type="text/javascript"></script><script>// if(cuslocked){window.location.href="http://www.google.com/";}else{window.location.href="http://www.stoneislandsshop.com/?keyword=";} // </script> - “cuslocked” – cookie that signals whether agent is googlebot or not
- [REDIRECT to a SCAM site] HTTP code 200, again – probably to avoid being detected as 30x redirect(s)
- SCAM webiste is loaded
As you can see, no 301 or 302 redirects.
Now we can create a list of all parties involved in this scheme and connect the dots:
- Victim[this might be you! 😉]
- Infected host [superbiketool.com] [some random, poor hacked website]
- Intermediate host [www.2015fashionnews.pw] [another poor random hacked website, or incautious scammer’s as in this case – explained later]
- Scam site [www.stoneislandsshop.com]
WHY this particular cloaking technique and how does scammer benefit from it?
- Scammer has set up a topic ecommerce website [brand fashion store that looks like a real one].
- Scammer knows that there are stores that are known for having that particular brand [victim], and that there are users performing a brand keyword queries on Google
- Scammer scrapes and recreates the whole victim website [with cloaking]
- Scammer creates redirects that point to scam sites [making sure that Google is not redirected]
Wanna know how it looks in practice?
- Victim site, but that might be you as well] is well known for selling products of Stone Island fashion brand (among others)
- Scammer has set up a SCAM site that mimics a popular brand name store [stoneislandsshop.com]
- Scammer has found/hacked some website[s] that is/are used as a cloaking host[s] site that will be indexed by googlebot [http://www.superbiketool.com/stois/stois2015042107.asp?*]
- Victim site is scraped and content is recreated on a cloaking website [with all the branded keywords]
- Googlebot indexes cloaked website [Googlebot can index content, as it’s not redirected as other user-agents]
- User performs branded query [related to a victim] on a Google and get scam website high in SERP [due to the fact that indexed content is really related to a victim/brand]
Example:
Google: “adidas black stan smith victim’s brand name”
Since query is performed including victim’s branded keyword “brand name”, scammer’s website is positioned very high in SERP.
How to protect and fix:
- check your backlinks regularly in Google Search Console [ex Google Webmasters Tools]
- use Google’s disavow Tool to exclude infected host’s backlinks
- report to Google webspam team using Webspam report form